DO COLLAGEN SUPPLEMENTS REALLY WORK?
In the last decade, collagen has become a very popular anti-ageing supplement promoted by celebrities and used to hydrate the skin, as well as reduce wrinkles and fine lines. But a growing body of research indicates that taking collagen peptides — also known as hydrolysed collagen or collagen hydrolysate — may have a wide range of health benefits beyond the cosmetic.
WHAT ARE COLLAGEN PEPTIDES?
Collagen is a protein that accounts for 25-30% of the total body protein in adults, making it the most abundant protein in the human body. It gives structure to your bones, tendons, skin, muscles, blood vessels and connective tissues, and is a major component of nails and hair. It is the most abundant protein in the body with humans having 28 different types of collagens; Type I and III for skin and cartilage being the most plentiful, as well as the type most commonly found in collagen supplements on the market.
Collagen is made up of 3 main building blocks, known as peptides: glycine, proline and hydroxiproline. Studies have shown that when taking collagen peptides, these amino acids, get absorbed and reach the dermis (the inner layer of your skin), stimulating your fibroblasts (skin cells that contribute to the formation of connective tissue) to produce collagen and hyaluronic acid.
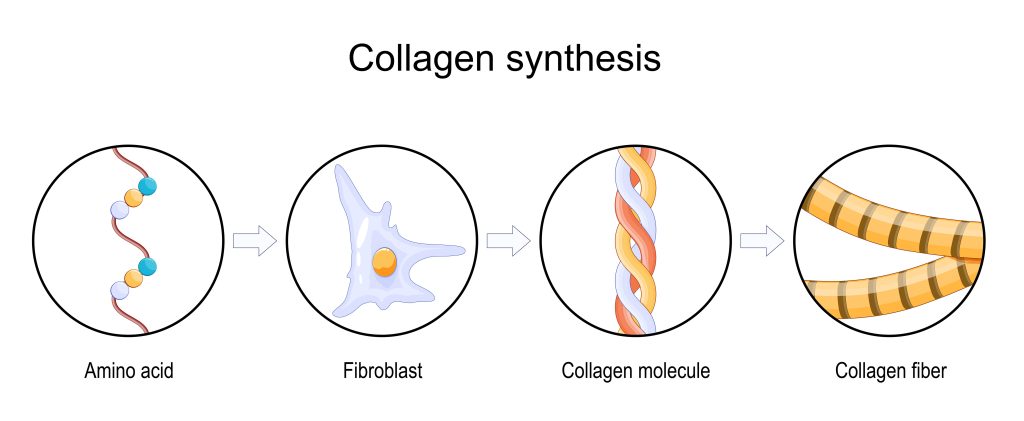
Collagen is a protein that accounts for 25-30% of the total body protein in adults, making it the most abundant protein in the human body.
WHAT IS COLLAGEN GOOD FOR?
- Improves skin hydration
- Reduces the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines
- Promotes hair & nail health
- Essential for strong, healthy bones
- Reduces joint pain and arthritis
- Boosts muscle mass and metabolism
- Supports weight loss by helping you feel fuller
- Promotes cardiovascular health
WHEN DOES COLLAGEN PRODUCTION DECLINE?
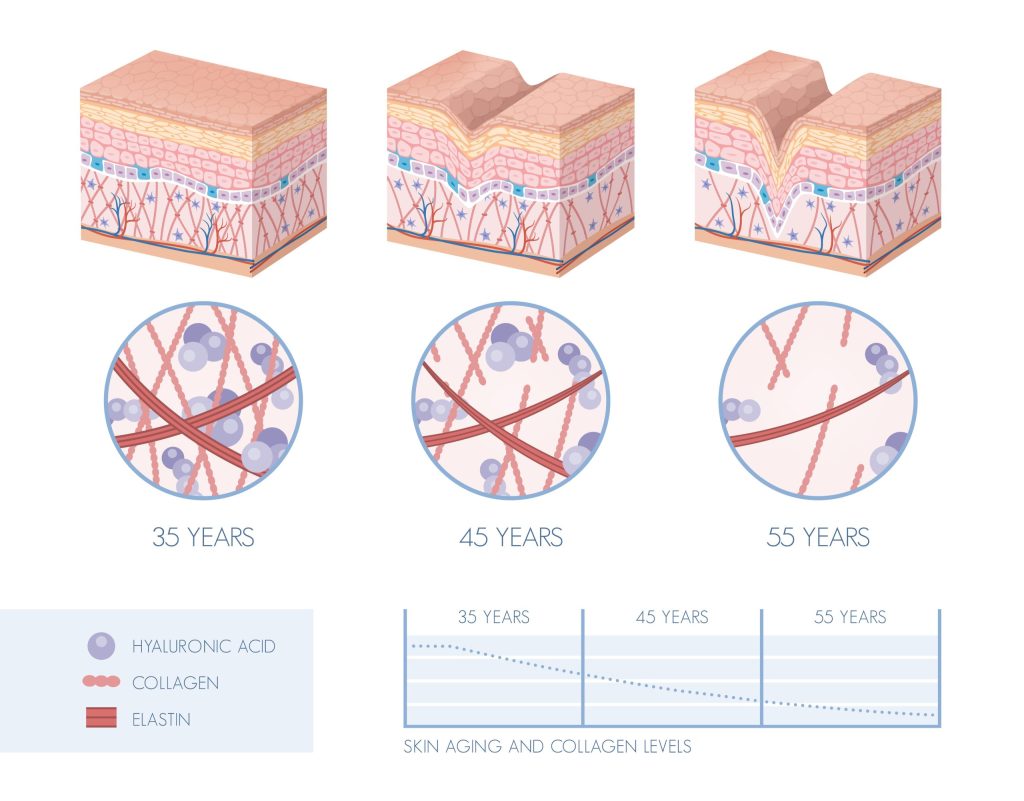
From age 25-30, collagen production starts to decline giving way to symptoms like wrinkles and decreased cartilage. Factors such as smoking, alcohol, pollution, sun exposure and a poor diet can interfere not just with collagen synthesis (production) but also the degradation of existing collagen in the skin, tendons, and capillaries. As you get older, changes in the structure of the dermis and epidermis occur. The collagen density decreases, and the dermal collagen network (fibres) becomes increasingly fragmented, given way to saggy skin and wrinkles. In parallel, the synthesis of new extracellular matrix components by dermal fibroblasts slows down.
FOODS HIGH IN COLLAGEN
To offset the body’s decline in collagen synthesis over time, there are natural ways to boost collagen production by eating foods that contain collagen, taking high quality collagen supplements and making certain changes to your lifestyle such as reducing alcohol consumption and smoking (both of which produce high amounts of free radicals that damage cells and break down collagen) as well as reducing sun exposure (UVA rays damage collagen fibers in the skin).
According to Dr. Mark Hyman, Medical Director of Cleveland Clinic’s Center for Functional Medicine, a poor diet is the main reason people lack collagen, and while taking in more foods and supplements containing collagen is important, you must also ensure you are getting enough nutrients to support the process of collagen synthesis which requires vitamin C, zinc and copper.
1. Bone broth
Bone broth is a great source of collagen, as well as containing several important amino acids. Bone broth is also available in powder form and makes an easy and healthy substitute to preparing the broth yourself from scratch.
2. Meat
Meats such as grass-fed beef, pork, lamb, chicken and even organs (like liver) contain high amounts of collagen because like us humans, these animals have plenty of connective tissues with collagen within them.
3. Cod
A great source of collagen for pescatarians is marine-sourced. Like most white fish, cod is packed with amino acids, such as glycine and proline. It’s also high in essential nutrients such as selenium, vitamin B6 and phosphorus. Where possible try to buy Alaskan cod instead of Atlantic cod, as the latter is a species that is overfished and considered less sustainable.
4. Eggs
Eggs and egg whites in particular, contain many of the amino acids that make up collagen, including glycine and proline. Using the whole egg instead of just the egg whites can also supply a steady stream of healthy fats and high-quality protein.

COLLAGEN SUPPLEMENTS
Supplementing your diet with collagen capsules or by adding collagen powder to your daily smoothie is a great way to increase collagen levels.
Collagen supplements are derived from hydrolysed collagen peptides and are always animal-sourced since collagen does not exist in plants.
If you are vegan, vegetarian, or looking to reduce the amount of animal products you eat, you can help boost your body’s collagen levels by supplementing your diet with products that naturally enhance your body’s own synthesis of collagen production for example: protein powders and collagen building protein peptides, essential amino acids (glycine, proline, hydroxyproline), silica, vitamin C and hyaluronic acid.
Find out if you have any nutritional deficiencies in your diet by booking an appointment, or a Functional Test which looks at your body’s biomarkers to detect imbalances, signs of potential illness and malabsorption of essential nutrients.
Your health. Your choice.
